In the ceaselessly evolving landscape of cybersecurity, the advent of artificial intelligence (AI) has introduced a double-edged sword. While AI offers powerful tools for defense, it has also fundamentally reshaped the offensive capabilities of malicious actors, giving rise to sophisticated and scalable AI-Enhanced Cyberattacks. As of mid-2025, these advanced threats leverage machine learning (ML) and generative AI to automate, personalize, and accelerate malicious activities, creating a more dynamic and perilous environment for individuals, businesses, and critical infrastructure worldwide. Understanding the mechanisms and implications of these AI-driven assaults is paramount for developing effective defensive strategies.
What Are AI-Enhanced Cyberattacks?
AI-Enhanced Cyberattacks refer to cyber threats where malicious actors leverage artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies to improve the speed, stealth, scale, and effectiveness of their attacks. Unlike traditional, manually executed attacks, AI-enhanced threats can adapt, learn, and operate with a level of autonomy that makes them harder to detect and defend against.
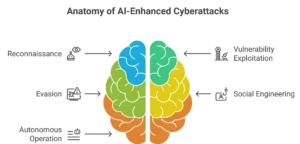
This enhancement can occur at various stages of an attack:
- Reconnaissance: Automating the collection and analysis of vast amounts of target information.
- Vulnerability Exploitation: Identifying and exploiting weaknesses more efficiently.
- Evasion: Developing malware that can learn to evade detection systems.
- Social Engineering: Crafting highly personalized and convincing phishing attempts.
- Autonomous Operation: Allowing malware to operate independently and adapt to network changes.
The goal is to increase the attacker’s chances of success while reducing the time, resources, and human intervention required for a successful breach.
How AI Fuels the Offensive: Key Modalities of AI-Enhanced Attacks
The integration of AI into cyber warfare enables attackers to automate and supercharge various phases of their operations. Here are some key modalities where AI-Enhanced Cyberattacks manifest :
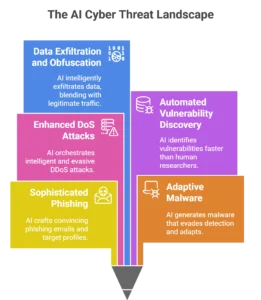
- Sophisticated Phishing and Social Engineering:
- Generative AI for Impersonation: Large Language Models (LLMs) enable attackers to generate highly convincing phishing emails, spear-phishing messages, and deepfake voice or video calls. These AI-crafted messages can mimic specific individuals or communication styles, bypassing traditional spam filters and human skepticism more effectively.
- Automated Target Profiling: AI algorithms can analyze publicly available information (social media, corporate websites) to build detailed profiles of targets, identifying their interests, relationships, and vulnerabilities, which are then exploited in personalized attacks.
- Adaptive Malware and Autonomous Hacking:
- Polymorphic Malware: AI can generate malware that constantly changes its code or behavior to evade detection by signature-based antivirus software. This adaptive nature makes it much harder to quarantine and analyze.
- Self-Learning Exploits: AI systems can learn from network responses to identify and exploit vulnerabilities in real-time, even in complex, unpatched systems. They can automate reconnaissance, vulnerability scanning, and exploit generation, shortening the attack chain.
- Enhanced Denial-of-Service (DoS/DDoS) Attacks:
- AI can orchestrate more intelligent and evasive DDoS attacks. Instead of simple volumetric attacks, AI can analyze network traffic patterns to identify weaknesses in defensive measures and dynamically adjust attack vectors, making it harder for mitigation systems to distinguish legitimate traffic from malicious floods.
- Automated Vulnerability Discovery:
- AI and ML algorithms can be trained on vast codebases and vulnerability databases to automatically identify logical flaws, security misconfigurations, and previously unknown (zero-day) vulnerabilities in software and systems faster than human researchers.
- Data Exfiltration and Obfuscation:
- AI can be used to intelligently exfiltrate data, blending malicious traffic with legitimate network activity to avoid detection. It can also help obfuscate malicious activities, making forensic analysis more challenging.
These methods highlight how AI significantly amplifies the capabilities of cybercriminals, state-sponsored actors, and hacktivists, demanding equally advanced defensive measures.
The Lifecycle of an AI-Enhanced Cyberattack
Understanding the typical stages of an AI-enhanced cyberattack provides insight into how these sophisticated threats operate:
This table illustrates the radical shift from reactive, manual processes to proactive, automated, and adaptive offensive capabilities.
Defensive Strategies Against AI-Enhanced Cyberattacks
Combating AI-Enhanced Cyberattacks requires a proactive, multi-layered defense strategy that also leverages AI. The principle here is “AI vs. AI.”
- AI-Powered Security Solutions:
- Advanced Threat Detection: Next-generation Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) and Extended Detection and Response (XDR) platforms use AI to analyze vast amounts of behavioral data, identify anomalies, and detect sophisticated threats that signature-based systems miss.
- Automated Incident Response: AI can automate parts of the incident response process, such as isolating infected systems, analyzing malware, and prioritizing alerts, speeding up response times.
- Behavioral Analytics: AI learns normal user and network behavior to spot deviations indicative of an attack, even from AI-generated anomalies.
- Network Traffic Analysis (NTA): AI analyzes network flows to detect subtle patterns associated with malicious activities, including C2 communications and data exfiltration.
- Reinforce the Human Element:
- Continuous Training: Regular, updated security awareness training for employees, including recognition of AI-generated phishing attempts (e.g., subtle inconsistencies, deepfake giveaways).
- Skilled Talent: Invest in training and recruiting cybersecurity professionals proficient in AI/ML concepts to effectively manage and fine-tune AI-powered defense systems.
- Human-in-the-Loop: While AI automates much, critical decision-making and ethical oversight must remain with human analysts.
- Robust Data and Infrastructure Security:
- Zero Trust Architecture: Assume no user or device is trustworthy by default. Verify everything before granting access. This minimizes the impact of a compromised credential.
- Strong Authentication: Implement Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) everywhere to mitigate compromised credentials.
- Patch Management & Vulnerability Scanning: Maintain rigorous patching schedules and continuous vulnerability scanning to reduce the attack surface.
- Security by Design: Integrate security considerations from the very beginning of the software development lifecycle (DevSecOps), applying “Shift Left Security” principles. For more on this, consider resources from the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) on Secure by Design.
- Threat Intelligence Sharing:
- Collaborate with industry peers, government agencies, and cybersecurity vendors to share threat intelligence, including new AI-enhanced attack vectors and mitigation strategies. Organizations like the Cyber Threat Alliance facilitate this vital information exchange.
The battle against AI-enhanced threats is an arms race where both sides leverage AI. A proactive, adaptive defense is the only way forward.
The Future of Cyber Conflict: A Continuous AI Arms Race
The rise of AI-Enhanced Cyberattacks is not a fleeting trend but a fundamental shift in the nature of cyber warfare. As AI capabilities continue to advance, we can expect:
- More Autonomous Attacks: Malicious AI systems capable of executing entire attack campaigns with minimal human intervention.
- Hyper-Personalization: Attacks that are so tailored to individual targets they become almost irresistible.
- Increasing Speed and Scale: The ability to launch complex attacks against millions of targets simultaneously and adapt in real-time.
- The Rise of “Explainable AI” in Defense: Security solutions will need to not only detect threats but also explain why something is a threat, helping human analysts understand complex AI-driven attacks.
- Focus on AI Model Security: Protecting the AI models themselves (from poisoning, adversarial attacks) will become a critical cybersecurity domain.
- International Cooperation and Regulation: A growing need for global frameworks and regulations to govern the use of AI in cyber warfare and prevent its misuse.
The cybersecurity landscape will increasingly be defined by a continuous AI arms race, where innovation in offensive AI is met by equally rapid advancements in defensive AI.
The emergence of AI-Enhanced Cyberattacks presents an unprecedented challenge to global cybersecurity. By leveraging the power of machine learning and generative AI, malicious actors are crafting threats that are more automated, sophisticated, and evasive than ever before. This new frontier demands a paradigm shift in our defensive strategies, requiring organizations to not only embrace AI-powered security solutions but also foster a culture of continuous vigilance, collaboration, and proactive “Shift Left Security.” The future of cybersecurity will be characterized by a dynamic interplay between offensive and defensive AI, underscoring the critical need for constant innovation and adaptation to protect our digital world.
Stay informed on the cutting edge of cybersecurity, AI, and digital defense strategies. Explore more expert analyses and insights on our platform at jurnalin.