The world of software development is undergoing a profound transformation, moving beyond traditional manual coding to embrace intelligent automation. At the heart of this shift is AI-Assisted Coding and Co-developers, a revolutionary paradigm where artificial intelligence tools work alongside human programmers to enhance efficiency, improve code quality, and accelerate innovation. As of mid-2025, these AI co-pilots are no longer futuristic concepts; they are actively integrated into developer workflows, generating code, identifying errors, and even suggesting design patterns, fundamentally redefining the nature of programming and setting the stage for an unprecedented era of human-AI collaboration in software creation.
The Dawn of AI-Assisted Coding
AI-Assisted Coding refers to the use of artificial intelligence tools and models to aid human developers in various stages of the software development lifecycle. This assistance can range from generating code snippets and suggesting autocompletions to identifying bugs, refactoring code, and even generating documentation.
The emergence of powerful large language models (LLMs) trained on vast repositories of code (like public GitHub repositories) has propelled AI-assisted coding into the mainstream. These AI “co-developers” function much like a highly intelligent pair programmer, providing real-time suggestions and solutions that accelerate development tasks. The goal is not to replace human programmers but to augment their capabilities, freeing them from repetitive tasks and allowing them to focus on higher-level problem-solving, architectural design, and creative innovation.
Evolution of Coding Tools : From IDEs to AI Co-developers
The evolution of coding tools has always been about enhancing developer productivity. We’ve moved from simple text editors to sophisticated Integrated Development Environments (IDEs) offering syntax highlighting, debugging tools, and version control integration. The advent of AI-Assisted Coding and Co-developers marks the next major leap.
This progression illustrates a shift from tools that assist with manual tasks to intelligent agents that actively participate in the creative and problem-solving aspects of coding.
How AI is Assisting Developers Today
Today’s AI-Assisted Coding and Co-developers are integrated into virtually every stage of the software development lifecycle, providing invaluable support:
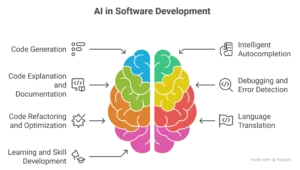
- Code Generation: This is perhaps the most well-known application. Tools can generate:
- Boilerplate Code: Standard structures, API calls, common functions.
- Complex Algorithms: Based on natural language prompts or existing code context.
- Tests: Automatically generating unit tests for existing functions.
- Intelligent Autocompletion : Beyond basic keyword completion, AI suggests entire lines, blocks of code, or even whole functions based on the developer’s intent and surrounding code, significantly speeding up typing and reducing syntax errors.
- Code Explanation and Documentation : AI can analyze existing codebases, explain complex functions, identify dependencies, and generate comprehensive documentation, which is crucial for onboarding new team members and maintaining legacy systems.
- Debugging and Error Detection : AI tools can analyze code in real-time to spot potential bugs, logical errors, security vulnerabilities, and performance bottlenecks, often before the code is even run or compiled. They can also suggest immediate fixes.
- Code Refactoring and Optimization : AI can identify areas where code can be made more efficient, readable, or maintainable, and even suggest optimized versions, adhering to best practices.
- Language Translation : AI can help translate code from one programming language to another, aiding in migration projects or supporting polyglot development teams.
- Learning and Skill Development : For junior developers, AI co-developers act as constant mentors, providing examples, explaining concepts, and guiding them towards best practices, accelerating their learning curve.
Popular tools like GitHub Copilot (powered by OpenAI’s Codex), Google’s Gemini Code Assistant, and various IDE integrations (e.g., within Visual Studio Code, IntelliJ IDEA) are leading this charge, demonstrating the practical utility of AI-Assisted Coding. For a deeper dive into the capabilities of these tools, an excellent resource is the GitHub Copilot documentation.
Key Benefits for Software Development Teams
The integration of AI-Assisted Coding and Co-developers yields substantial benefits for individual programmers and entire software development organizations:
These advantages collectively position AI-Assisted Coding and Co-developers as indispensable tools for modern software engineering.
Challenges and Considerations
While the benefits are clear, the widespread adoption of AI-Assisted Coding and Co-developers also introduces several important challenges and considerations that development teams must address.
- Accuracy and Reliability: AI models, while powerful, are not infallible. Generated code may contain subtle bugs, security vulnerabilities, or simply not align perfectly with the developer’s intent. Human oversight and rigorous testing remain critical.
- Security Implications: Training data for AI models often comes from public repositories, which may include insecure or vulnerable code. If AI generates code based on these patterns, it could inadvertently introduce security flaws into new applications. Data privacy concerns also arise if proprietary code is used to fine-tune AI models.
- Ethical Dilemmas and Bias: AI models can perpetuate biases present in their training data, potentially leading to unfair or discriminatory outcomes in the logic of the generated code. Questions also arise about the intellectual property rights of AI-generated code, especially if it closely resembles existing proprietary code.
- Over-Reliance and Skill Erosion: Excessive reliance on AI could potentially lead to a degradation of fundamental coding skills among developers. If AI always provides the answer, will developers still develop the deep problem-solving abilities needed for complex, novel challenges?
- Integration Complexity: Integrating AI tools seamlessly into existing development workflows, IDEs, and version control systems can still present challenges.
- Cost and Resource Demands: Running and fine-tuning advanced AI models for coding assistance can be computationally expensive, requiring significant cloud resources or powerful local hardware.
- Maintaining Context: While improving, AI models can sometimes struggle to maintain a complete understanding of a large, complex codebase or project-specific nuances, leading to less optimal or irrelevant suggestions.
Navigating these challenges requires a balanced approach, where AI is viewed as a powerful assistant rather than a replacement, emphasizing continuous learning, robust testing, and strong governance policies for AI-generated code. The importance of human judgment and critical thinking remains paramount. For insights on ethical considerations, explore resources like the IEEE Global Initiative on Ethics of Autonomous and Intelligent Systems.
The Future of Software Development: Human-AI Collaboration
The trajectory of AI-Assisted Coding and Co-developers suggests a future where the lines between human and machine contributions in software creation become increasingly blurred, leading to a truly collaborative development environment.
- Smarter, More Context-Aware AI: Future AI co-developers will have a deeper understanding of entire codebases, architectural patterns, and project requirements, enabling them to provide more precise, relevant, and proactive assistance.
- AI for Entire Software Lifecycle: Beyond just code generation, AI will play a greater role in requirements gathering, architectural design, automated testing, deployment, and even ongoing maintenance and performance optimization.
- Personalized AI Assistants: AI tools will learn individual developer preferences, coding styles, and common errors, offering highly personalized assistance that adapts to each programmer’s unique workflow.
- Low-Code/No-Code Empowerment: AI will further democratize software creation, enabling non-developers to build sophisticated applications through natural language instructions, effectively turning anyone into a “citizen developer.”
- The Rise of “Prompt Engineering” for Code: The ability to craft clear, effective prompts to guide AI models will become a crucial skill for developers, shifting focus from raw coding to instructing intelligent systems.
- New Developer Roles: While some tasks may be automated, new roles will emerge, such as AI trainers, AI ethics specialists for code, and “AI whisperers” who specialize in maximizing the output of AI co-developers.
- Enhanced Security Through AI: AI will also be a key tool in defending against AI-generated malicious code, creating a dynamic arms race in cybersecurity.
The future of software development will not be about humans or AI, but about humans and AI collaborating to build more complex, efficient, and innovative software solutions than ever before.
The integration of AI-Assisted Coding and Co-developers is irrevocably transforming the landscape of software development. By automating routine tasks, improving code quality, and accelerating development cycles, these intelligent tools empower programmers to achieve unprecedented levels of productivity and creativity. While the journey requires navigating challenges related to accuracy, security, and ethical considerations, the path forward is clear: AI will continue to evolve as an indispensable partner in the coding process. Embracing this new era of human-AI collaboration will be paramount for developers and organizations alike to stay competitive and innovative in the ever-demanding world of software creation.
Eager to stay ahead in the rapidly evolving tech landscape, including the latest in AI and software development? Discover more expert insights and analysis on our platform at jurnalin!